Steps for the significance of Natural Account Qualifier
1. Types of Natural Accounts
and their Details
2. Flex field Qualifiers Setup
3. How and where the type of account was assigned to Natural segment values in oracle apps.
- Types of Natural Accounts and their
Details
There are 5 natures of account. Every account can have any
one nature and that’s why we can also call it natural account.
These natures are:
1. Assets
2. Liabilities
3. Revenue
4. Expenses
5. Owner’s Equity
ASSET: Literally asset is anything which is valuable to a person, organization, or any entity. For example, we say that “his quick learning ability is an asset to him” or “Her writing ability is her asset”. Why do we say that? Because quick learning skill or writing ability adds value to a person. A writer sells his writing skills to earn money, similarly in terms of business anything which is valuable to a business is the asset.
Say your
organization is a pharmaceutical and manufactures Medicines, then all the chemicals used to manufacture medicine is your asset or in other words
the Raw Material is your asset. The cash your organization own is an asset
because it can be used to buy items or pay your employee who
in turn are used to run your business. There are different types of assets, the
broader categories of asset are Current Asset and Fixed, but let’s not discuss it
here. For now, it is enough to know that asset is anything which is valuable to
your organization.
Asset INCREASES
when it is Debited and DECREASES when Credited.
Any organization which is registered with the government and exists as Legal Entity is obligated to disclose its Assets on the balance sheet to the government and its Creditors. You might ask Who are creditors and why is it that an organization is obligated to disclose asset to them? With Creditor comes in the liability.
LIABILITY: Comes from the
word “Liable”. Literal meaning of Liable is “to be
obligated”, “to be responsible” or “Legally responsible”.
In terms of accounting, you become liable, responsible to pay when you buy or
purchase anything from another entity. You are liable to
compensate whatever you’ve bought. Generally, an organization records its
liability and pays it afterward. Again, there are different types of
liabilities like Short Term Liability and Long-Term Liability.
Liability INCREASES when it is Credited and DECREASES when Debited.
OWNER’S EQUITY: This is the share of owner in the business. Equity INCREASES when it is Credited and DECREASES when Debited.
REVENUE: It is the total gain before
inducting any expense. It is mostly associated with the Asset. When any
organization sell goods or renders its services, it records an increase in
Asset and with this increase comes the gain it has made from selling the goods
or services. This gain is called Revenue or Income.
Revenue INCREASES
when it is Credited and DECREASES when Debited.
Revenue is not
displayed in Balance Sheet. They are reflected in Owner’s Equity.
EXPENSE: Any payment made is an expense. How are payments made? Either by Cash or Credit which eventually means Cash. So redefining Expense “The outflow of cash to any person or organization for its supplied Goods or rendered Services”. We incur expenses daily, for example, taxi fare is an expense, dine-out payments are expenses. Expenses are associated with Liability. Whenever an organization books a liability, it is mostly against some expense. There is different type of expense
Expense INCREASES
when it is Debited and DECREASES when Credited.
Following table
shows the Tabular form of the effect
|
Nature |
DEBIT |
CREDIT |
|
Asset |
Increase (+) |
Decrease (-) |
|
Liability |
Decrease (-) |
Increase (+) |
|
Equity |
Decrease (-) |
Increase (+) |
|
Revenue |
Decrease (-) |
Increase (+) |
|
Expense |
Increase (+) |
Decrease (-) |
Flex
field Qualifiers Setup:
Flex
field Qualifiers are registered as part of Flex field Registration.
Navigation:
Flex field Registration Form
Query For the title
“Accounting Flex field”
Then Click
the Qualifiers button in the above form to check
the registration of Flex field Qualifiers and Segment
Qualifiers.
To check the types
of Segment Qualifiers allowed Query for the Quick code type mentioned in
the above screenshot in quick codes form.
In Oracle General Ledger, when we attach the “Natural Account” Flex field Qualifier to a segment. System attaches the above set of nature on the Value form. When we add the Natural Account Value, we have to define the nature of the account as well.
How and where the type of account (Segment Qualifiers) was assigned to Natural segment values in oracle apps.
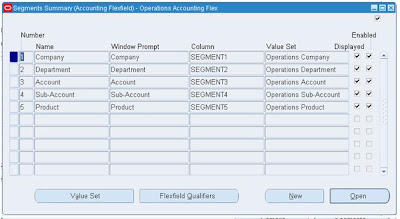
Query for the title “Accounting
Flex field” in the SEGMENTS Form
Click on the segments button
in the above form to view segment details
Choose the appropriate
segment and click the “Flex field Qualifiers” button to view the below screen
Close the form and open the
“values” to check the values attached to segment
Query for the Accounting
Flex field
Choose the segment which has flex field Qualifier as “Natural Account” and then click the “Values, Hierarchy, Qualifiers” tab to check the segment qualifiers assignment.










No comments:
Post a Comment